Developing documents(已废弃)
API Invocation Method Instructions
APIs on TOP are invoked based on the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). The developer (such as the ISV) can directly use the official SDK provided by the TOP to invoke an API. This official SDK supports multiple languages and various features, such as request encapsulation, signature encryption, response interpretation, and performance optimization. The ISV can also encapsulate an HTTP request in compliance with TOP protocols to invoke an API. The following describes the principles of API invocation based on HTTP request encapsulation.
Invocation Process
In compliance with TOP protocols, the API invocation process is as follows: Fill in parameters. > Generate a signature. > Encapsulate an HTTP request. > Initiate the HTTP request. > Receive an HTTP response. > Interpret json/xml results, as shown in the following figure. You can choose developing your own HTTP invocation and interpretation module or using TOP SDK to interact with TOP server.
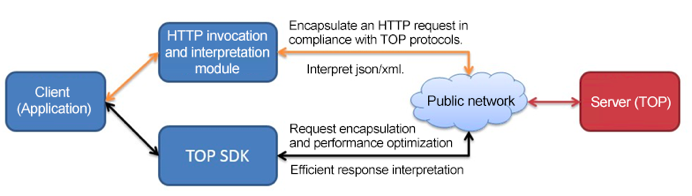
Invocation Entry
Based on the service URL used to invoke APIs, the AliExpress open platform currently provides three environments for ISVs: formal test environment, formal environment, and overseas environment.
- Formal test environment: refers to a formal simulation environment used before the ISV software is put online. An ISV can use this environment after successfully creating an application. This environment limits the API invocation quantity to 5,000 times/day and allows a maximum of five users to grant authorization. APIs that can be invoked are consistent with the permission capability of the corresponding application.
- Formal environment: refers to an environment used after the ISV software is put online. The entry of this environment is the same as that of the formal test environment. However, a traffic limit will be enabled after an application is put online. The specific traffic limit is related to the category of the corresponding application. For example, the API invocation quantity of a Service Market application is limited to 1,000,000 times/day.
- Overseas environment: refers to a type of formal environment offered to overseas ISVs (especially those in European and American countries). As for overseas ISVs, this environment can provide doubled performance than the domestic environment.
| Invocation Environment | Service URL (HTTP) | Service URL (HTTPS) |
|---|---|---|
| Formal environment | http://gw.api.taobao.com/router/rest | https://eco.taobao.com/router/rest |
| Overseas environment | http://api.alibaba.com/router/rest (recommended) http://api.taobao.com/router/rest | https://api.alibaba.com/router/rest (recommended) https://api.taobao.com/router/rest |
Public Parameter
Public parameters must be imported if any one of APIs is invoked. The following table lists all public parameters that are currently supported.
| Parameter Name | Parameter Type | Mandatory or Optional | Parameter Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| method | String | Mandatory | Indicates the API name. |
| app_key | String | Yes | Indicates the AppKey allocated by the TOP to an application. An ISV can choose Open Platform Console > Application Management > Overview to check the AppKey and AppSecret of the formal environment. |
| session | String | Yes | Indicates the authorization granted by the TOP to an application after a user logs in and grants authorization successfully. For details, click here. |
| timestamp | String | Yes | Indicates the time stamp in the format of yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss and in the time zone of GMT+8. For example, 2016-01-01 12:00:00. The Taobao API server allows a maximum time error of 10 minutes for a request from a client. |
| format | String | No | Indicates the response format. The default value is xml. The value can be set to xml or json. |
| v | String | Yes | Indicates the API protocol version. The value can be set to 2.0. |
| simplify | Boolean | No | Indicates whether the simplified JSON return format is used. This parameter is valid only if format is set to json. The default value is false. |
| sign_method | String | Yes | Indicates the signature digest algorithm. The value can be set to hmac or md5. |
| sign | String | Yes | Indicates the obtained signature of API input parameters. For details about the signature algorithm, see the following description. |
Service Parameter
In addition to public parameters to be imported during API invocation, service-level parameters (if any) of an API must also be imported. For details about service parameters of each API, see API Document.
Signature Algorithm
To prevent data from being tampered with maliciously by a hacker during API invocation, each request for API invocation must carry a signature. The TOP server verifies the signature based on request parameters and rejects the request carrying an invalid signature. Currently, the TOP supports two signature algorithms: MD5(sign_method=md5) and HMAC_MD5(sign_method=hmac). The signature process is generally described as follows:
- Sort all request parameters of an API (including public parameters and service parameters, but excluding the sign parameter and parameters of the byte[] type) based on the sequence of their parameter names in the ASCII tabl. For example, parameters foo:1, bar:2, foo_bar:3, and foobar:4 are sorted as follows: bar:2, foo:1, foo_bar:3, foobar:4.
- Splice the sorted parameter names and values together to obtain a character string. For example, the character string obtained in the preceding example is bar2foo1foo_bar3foobar4.
- Encode the spliced character string based on UTF-8 encoding and use a signature algorithm to produce a digest for the encoded byte stream. If the MD5 algorithm is used, add the secret value of the corresponding application before and after the spliced character string, and then produce a digest, for example, md5(secret+bar2foo1foo_bar3foobar4+secret). If the HMAC_MD5 algorithm is used, initialize the digest algorithm based on the secret value of the corresponding application, and then produce a digest, for example, hmac_md5(bar2foo1foo_bar3foobar4).
- Denote the byte stream obtained after the digest in hexadecimal, for example, hex(“helloworld”.getBytes(“utf-8”)) = “68656C6C6F776F726C64”.
Note: Both MD5 and HMAC_MD5 digest algorithms produce a 128-bit value represented in hexadecimal. As each hexadecimal character represents four bits, the length of the signature character string is fixed to 32 hexadecimal characters.
Java Signature Sample Code
public static String signTopRequest(Map<String, String> params, String secret, String signMethod) throws IOException {
//Step 1: Check whether parameters have been sorted.
String[] keys = params.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
Arrays.sort(keys);
//Step 2: Splice all sorted parameter names and values together.
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
if (Constants.SIGN_METHOD_MD5.equals(signMethod)) {
query.append(secret);
}
for (String key : keys) {
String value = params.get(key);
if (StringUtils.areNotEmpty(key, value)) {
query.append(key).append(value);
}
}
//Step 3: Use the MD5 or HMAC_MD5 algorithm to encrypt the spliced character string.
byte[] bytes;
if (Constants.SIGN_METHOD_HMAC.equals(signMethod)) {
bytes = encryptHMAC(query.toString(), secret);
} else {
query.append(secret);
bytes = encryptMD5(query.toString());
}
//Step 4: Convert binary characters into capitalized hexadecimal characters. (A correct signature must be a character string consisting of 32 capitalized hexadecimal characters. This step is performed as required.)
//return byte2hex(bytes);
}
public static byte[] encryptHMAC(String data, String secret) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = null;
try {
SecretKey secretKey = new SecretKeySpec(secret.getBytes(Constants.CHARSET_UTF8), "HmacMD5");
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance(secretKey.getAlgorithm());
mac.init(secretKey);
bytes = mac.doFinal(data.getBytes(Constants.CHARSET_UTF8));
} catch (GeneralSecurityException gse) {
throw new IOException(gse.toString());
}
return bytes;
}
public static byte[] encryptMD5(String data) throws IOException {
return encryptMD5(data.getBytes(Constants.CHARSET_UTF8));
}
public static String byte2hex(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder sign = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(bytes[i] & 0xFF);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
sign.append("0");
}
sign.append(hex.toUpperCase());
}
return sign.toString();
}
C# Signature Sample Code
public static string SignTopRequest(IDictionary<string, string> parameters, string secret, string signMethod)
{
//Step 1: Sort the dictionary based on the alphabetical order of Key.
IDictionary<string, string> sortedParams = new SortedDictionary<string, string>(parameters, StringComparer.Ordinal);
IEnumerator<KeyValuePair<string, string>> dem = sortedParams.GetEnumerator();
//Step 2: Splice all sorted parameter names and values together.
StringBuilder query = new StringBuilder();
if (Constants.SIGN_METHOD_MD5.Equals(signMethod))
{
query.Append(secret);
}
while (dem.MoveNext())
{
string key = dem.Current.Key;
string value = dem.Current.Value;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(key) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(value))
{
query.Append(key).Append(value);
}
}
//Step 3: Use the MD5 or HMAC_MD5 algorithm to encrypt the spliced character string.
byte[] bytes;
if (Constants.SIGN_METHOD_HMAC.Equals(signMethod))
{
HMACMD5 hmac = new HMACMD5(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(secret));
bytes = hmac.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(query.ToString()));
}
else
{
query.Append(secret);
MD5 md5 = MD5.Create();
bytes = md5.ComputeHash(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(query.ToString()));
}
//Step 4: Convert binary characters into capitalized hexadecimal characters.
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.Length; i++)
{
result.Append(bytes[i].ToString("X2"));
}
return result.ToString();
}
For details about signature sample code in other languages, see source code of the TOP official SDK.
Invocation Example
The following uses the API aliexpress.logistics.redefining.getonlinelogisticsinfo (obtain the online logistics information) as an example. The procedure for invoking this API is as follows:
1. Set parameter values.
Public parameters:
- method = “aliexpress.logistics.redefining.getonlinelogisticsinfo”
- app_key = “12345678”
- session = “test”
- timestamp = “2016-01-01 12:00:00”
- format = “json”
- v = “2.0”
- sign_method = “md5”
Service parameters:
- international_logistics_id = “LP00038357949881”
- logistics_status = “INIT”
2. Sort parameters based on the sequence of their parameter names in the ASCII chart.
- app_key = “12345678”
- format = “json”
- international_logistics_id = “LP00038357949881”
- logistics_status = “INIT”
- method = “aliexpress.logistics.redefining.getonlinelogisticsinfo”
- session = “test”
- sign_method = “md5”
- timestamp = “2016-01-01 12:00:00”
- v = “2.0”
3. Splice parameter names and values.
app_key12345678formatjsoninternational_logistics_idLP00038357949881 logistics_statusINITmethodaliexpress.logistics.redefining.getonlinelogisticsinfosessiontestsign_methodmd5timestamp2016-01-01 12:00:00v2.0
4. Generate a signature.
Assume that secret of the application is helloworld. The obtained signature is as follows: hex(md5(helloworld+Sorted and spliced parameter names and values+helloworld)) = “66987CB115214E59E6EC978214934FB8”.
5. Encapsulate an HTTP request.
Perform URL encoding for all parameter names and values based on UTF-8 encoding. The sequence of parameters can be random, but the sign parameter must be included. Then, use the GET or POST method (containing parameters of the byte[] type) to initiate the HTTP request. For example:
http://gw.api.taobao.com/router/rest?method=aliexpress.logistics.redefining.getonlinelogisticsinfo&app_key=12345678&session=test×tamp=2016-01-01 12:00:00&format=json&v=2.0&sign_method=md5&international_logistics_id=LP00038357949881&logistics_status=INIT&sign=66987CB115214E59E6EC978214934FB8
Important Notes
- All requests and response data are encoded in UTF-8 format. URL encoding is required for all parameter names and parameters in a request URL. If Content-Type is application/x-www-form-urlencoded in a request, URL encoding is required for all parameter values in the HTTP body. If a request is in multipart/form-data format, encoding is not required for parameter values of each form field, but charset of each form field must be set to utf-8.
- If a request URL spliced by parameter names and values is shorter than 1,024 characters, this request can be initiated by means of the GET method. If parameters of the byte[] type are included or a spliced request URL is excessively long, this request must be initiated by means of the POST method. The POST method applies to the initiation of requests for all APIs.
- Signature generation (sign) is required only if an ISV does not use the TOP official SDK to invoke an API. If the TOP official SDK is used, the SDK will automatically generate a signature.
